The Ultimate Guide to CNC Bits for Router – Types, Uses, and Tips for Precision Cutting
Website Admin2024-10-21T22:07:15-06:00The Complete Guide to CNC Router Bits
Contents
ToggleWhat is a CNC Router?
A CNC (Computer Numerical Control) router is a machine that cuts materials based on pre-programmed designs. From furniture making to intricate carvings, CNC routers offer speed, accuracy, and repeatability. The key component in delivering these results is the bit. The bit is the actual tool that contacts and cuts the material, shaping it into your desired design. With so many types of bits available, it’s essential to understand which bit to use and why.
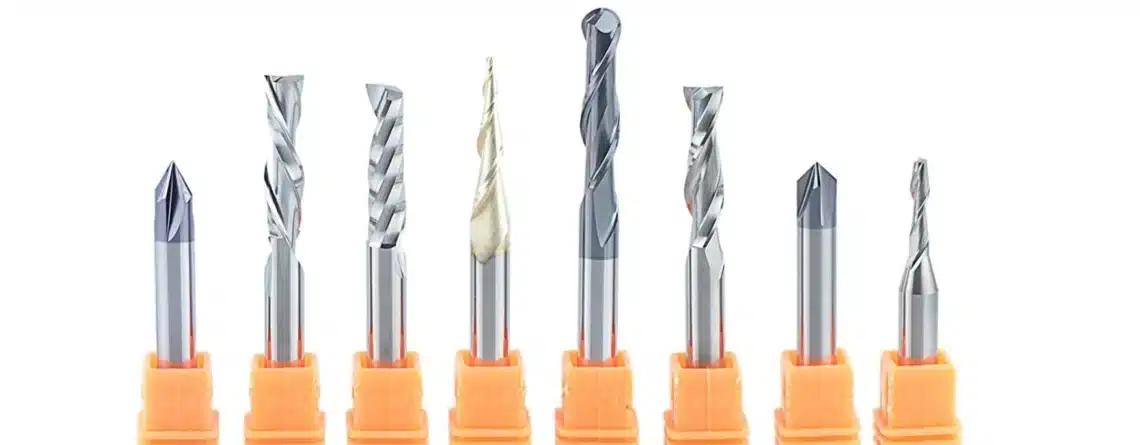
1. Overview of CNC Router Bits
CNC router bits are specialized cutting tools designed for use in CNC machines. They come in various shapes and sizes, each optimized for specific tasks like cutting, engraving, or shaping. Choosing the right bit ensures smooth cuts, minimizes wear and tear on your machine, and helps you achieve the desired finish.

There are numerous factors to consider when choosing a bit, such as the material being cut, the desired edge finish, and the type of cut (whether it’s a plunge, groove, or surface pass). Let’s break down the most common types of CNC router bits and their applications.
2. Types of CNC Router Bits
End Mill Bits
End mill bits are among the most versatile and commonly used in CNC routing. They have a flat cutting end that makes them ideal for making cuts with flat bottoms.
- Applications: These bits are excellent for pocketing, contouring, and general-purpose cutting on flat surfaces.
- Variants: Available in square, corner-radius, and ball-end styles, each serves different cutting needs.
The key benefit of end mills is their precision when cutting straight lines or flat surfaces. When you need to create square corners or pockets in your workpiece, an end mill bit will provide the sharp, defined edge required.
Ball Nose Bits
Ball nose bits have a rounded cutting tip, making them the preferred tool for 3D contouring and carving. The rounded shape prevents sharp edges from being left behind and allows for smooth, continuous cuts on curved surfaces.
- Applications: Ideal for 3D carving, creating contours, and working on intricate designs where a softer edge is required.
Ball nose bits shine in applications where you need smooth transitions between different depths or gradients, such as topographical maps, custom signs, or sculptures.
V-Bits
V-bits feature a pointed tip and are primarily used for engraving and detailed work. The “V” shape allows them to cut narrow, sharp grooves, making them perfect for intricate designs.
- Applications: Sign-making, engraving, and lettering.
They’re commonly used in sign-making to create crisp, clean lines or in engraving projects where precision is key. The angle of the V-bit also affects the depth and width of the cuts, allowing for varied design options.
Upcut and Downcut Bits
Upcut and downcut bits are distinguished by the direction in which they remove material.
- Upcut Bits: Remove chips by pulling them upward, ensuring excellent material removal and preventing overheating.
- Downcut Bits: Push chips downward, creating cleaner edges on the top surface of the material.
- Applications: Upcut bits are great for deep cuts where efficient chip removal is crucial, while downcut bits are best for keeping the top surface of the material clean and free of tear-out.
Compression Bits
Compression bits are a hybrid design, combining both upcut and downcut flutes. The unique design pulls chips up from the bottom of the material and pushes chips down from the top, making it perfect for working with laminated materials like plywood and MDF.
- Applications: Ideal for cutting laminated materials, as they prevent tear-out on both the top and bottom surfaces.
Specialty Bits
There are a variety of specialty bits designed for niche applications. Some examples include:
- Surfacing Bits: Used to flatten or “surface” the material.
- Dovetail Bits: For creating dovetail joints in cabinetry and furniture making.
- Corner Round Bits: To soften the edges of your material.
Each of these bits offers unique advantages for specific tasks and is worth considering based on the project at hand.
3. Materials and Coatings of CNC Router Bits
The material and coating of a router bit have a significant impact on its durability, precision, and effectiveness. Here are the most common options:
Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide bits are the most popular for CNC routing due to their hardness and longevity. They maintain a sharp edge longer than other materials, making them ideal for cutting wood, plastic, and soft metals.
High-Speed Steel (HSS)
While less durable than carbide, HSS bits are a cost-effective option for beginners or those working with softer materials like wood. They tend to dull more quickly but are easier to sharpen.
Diamond-Coated Bits
Diamond-coated bits are the top-of-the-line in terms of durability and precision. These bits are primarily used for cutting hard materials like stone, glass, or composites.
Coatings
Router bits often come with coatings to extend their life and improve performance. Common coatings include:
- Titanium Nitride (TiN): Increases hardness and reduces friction.
- Zirconium Nitride (ZrN): Improves wear resistance.
- Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC): Offers extreme hardness and is used in high-performance applications.
4. Choosing the Right Bit for Your Project
When selecting a bit, consider the following factors:
Material to Be Cut
Different materials require different bits. For example, cutting aluminum requires a bit with a lower flute count and high chip removal capabilities, while cutting wood may require a bit with more flutes for a smoother finish.
Desired Finish
If you’re aiming for a smooth, polished edge, you’ll want a bit with more flutes. For rough cuts or fast material removal, a bit with fewer flutes will be more efficient.
Bit Size and Flute Configuration
Bit size and flute count impact both the speed and quality of the cut. Fewer flutes remove material quickly, but more flutes leave a smoother finish.
5. Maintenance and Care of CNC Router Bits
To get the most out of your bits, proper maintenance is crucial.
Cleaning
After each use, clean your bits to remove any buildup of debris or resin. A simple wire brush or solvent can help maintain the cutting edge.
Sharpening
Even the most durable bits will dull over time. You can either sharpen them yourself with specialized tools or take them to a professional.
Storage
Store your bits in a dry, organized environment. Avoid letting them clank against each other, as this can dull or damage the cutting edges.
6. Advanced Tips for Maximizing Efficiency with CNC Router Bits
Optimal Feed Rate and RPM Settings
Finding the right feed rate (the speed at which the material moves through the router) and RPM (rotations per minute) is essential for preventing bit breakage and achieving clean cuts.
Trial Runs and Prototyping
Always test your settings on a scrap piece of material before running the actual job. This helps avoid costly mistakes and allows you to fine-tune your machine settings.
7. Best Practices and Safety Tips
Safety First
Always wear protective eyewear, gloves, and hearing protection when operating a CNC machine. Bits can break, and debris can fly unexpectedly.
Setting Up Your CNC Machine for Success
Ensure your bit is properly seated in the collet and that your machine is calibrated correctly. A poorly installed bit can lead to inaccurate cuts or even machine damage.
8. Emerging Technologies in CNC Router Bits
As CNC technology evolves, so do router bits. Some innovations include:
- Custom 3D-Printed Bits: Tailored designs that optimize cutting for specific materials.
- Smart Bits: Technology that monitors bit wear and adjusts machine parameters automatically for maximum efficiency.
Conclusion
Selecting the right CNC router bit is crucial to the success of your project. Whether you’re cutting wood, metal, or composites, understanding the different types of bits and their uses can help you achieve professional-quality results. With the right maintenance and setup, you can extend the life of your bits and get the most out of your CNC router.